Evaluation of FLAI AI Classification on LiDAR Data Collected with the AISPECO Heliux LITE System and RIEGL VQ-580 II-S
A joint technical analysis of AI-based point-cloud classification across multiple environments and flight conditions
AI-based classification of airborne LiDAR point clouds
Four environments: rural, dense urban, industrial, powerline corridor
Two flight altitudes and varying point densities
Processing-time benchmarks and indicative pricing context
Independent engineering observations from AISPECO and FLAI
Interactive 3D dataset examples available online
This white paper presents a joint technical study by AISPECO and FLAI examining AI-based semantic classification of airborne LiDAR data under real-world operating conditions.
LiDAR datasets were collected using the AISPECO Heliux LITE system integrated with a RIEGL VQ-580 II-S sensor and processed using FLAI’s AI classification workflow. The analysis focuses on how classification performance is influenced by point density, scene complexity, and object scale across multiple environments and flight configurations.
In addition to classification results, the study provides practical operational context, including indicative processing times and pricing considerations, along with independent engineering observations from both teams. The aim is to give mapping professionals a realistic reference for evaluating automated LiDAR classification in production workflows.
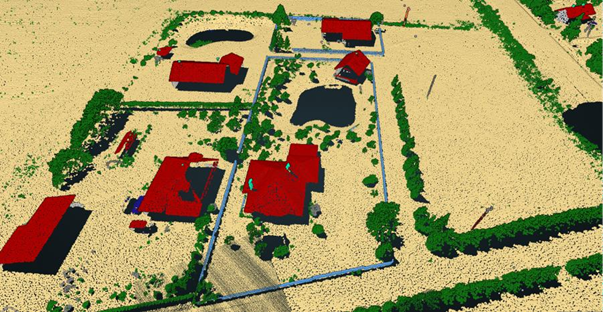
Classification results in a rural area, showing good detection of buildings vegetation and fence
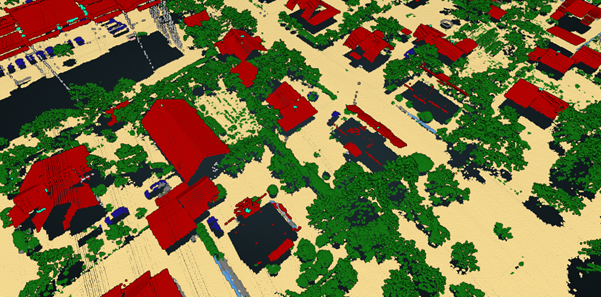
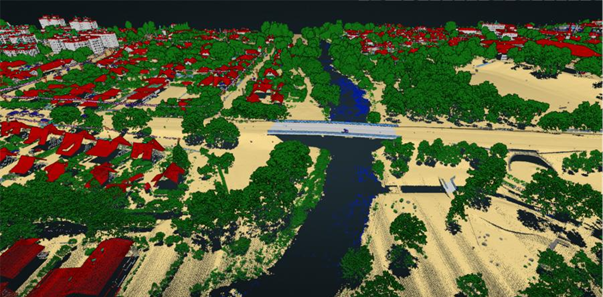
Classification results in a dense urban area, showing strong performance on residential neighborhoods and large structures, accurate classification of buildings near or under vegetation, and successful building detection of low-reflection roofs
